Production-Ready External Auth: CORS, Token Refresh & API Implementation with Wasp
Table of Contents
- Step 1: Implementing CORS Middleware
- Step 2: Implementing API Endpoints
- Step 3: Token Validation and Shared Utilities
- Step 4: Complete Environment Configuration
- Step 5: Chrome Extension Integration
- Testing the Complete Flow
- Troubleshooting
- About the Author
Step 1: Implementing CORS Middleware
Replace the placeholder middleware with real CORS logic. Update app/src/auth/external/middleware.ts:
import type { MiddlewareConfigFn } from "wasp/server";
import cors from "cors";
const ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS =
process.env.ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS?.split(",")
.map(id => id.trim())
.filter(Boolean) || [];
const isDevelopment = process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production";
/**
* Validate if an origin is an allowed Chrome extension
*/
function isValidExtensionOrigin(origin: string): boolean {
if (!origin.startsWith("chrome-extension://")) {
return false;
}
const extensionId = origin.replace("chrome-extension://", "").split("/")[0];
return ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS.includes(extensionId);
}
/**
* CORS middleware for external API endpoints
* Add any rate limiting in here too
*/
export const externalApiMiddleware: MiddlewareConfigFn = middlewareConfig => {
middlewareConfig.set(
"cors",
cors({
origin: (origin, callback) => {
// Require allowlist in all environments
if (ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS.length === 0) {
console.error(
"[CORS] No extension IDs configured in ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS"
);
return callback(
new Error("Extension allowlist not configured"),
false
);
}
// During development, log more details for debugging
if (isDevelopment) {
console.log(`[DEV CORS] Checking origin: ${origin || "same-origin"}`);
console.log(`[DEV CORS] Allowed IDs:`, ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS);
}
// Allow same-origin requests (from your Wasp app)
if (!origin) {
if (isDevelopment) {
console.log("[DEV CORS] Allowing same-origin request");
}
return callback(null, true);
}
// Check against extension allowlist
if (isValidExtensionOrigin(origin)) {
console.log(`[CORS] Allowed extension: ${origin}`);
return callback(null, true);
}
// You can add other allowed origins here (e.g., mobile apps)
console.warn(`[CORS] Rejected origin: ${origin}`);
callback(new Error("Not allowed by CORS"), false);
},
credentials: true, // Allow cookies for session-based auth
methods: ["POST", "GET", "OPTIONS"],
allowedHeaders: ["Content-Type", "Authorization", "X-Device-ID"],
exposedHeaders: ["Content-Type"],
})
);
return middlewareConfig;
};
Development and Production Behavior:
The allowlist is required in both development and production. This catches misconfiguration early and enforces production-like security from the start. It also prevents accidental deployments without a properly configured allowlist.
During development, the middleware provides additional logging to help with debugging, but it still enforces the same allowlist. To test with your extension during development, simply add your development extension ID to the ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS environment variable.
Why require the allowlist in development?
- Catches misconfiguration early: You’ll discover environment variable issues during development, not in production
- Production-like security: Your development environment behaves the same as production
- Prevents accidents: No risk of deploying with an overly permissive development configuration
Step 2: Implementing API Endpoints
Now let’s implement the actual API logic. Here’s how the three endpoints work together:
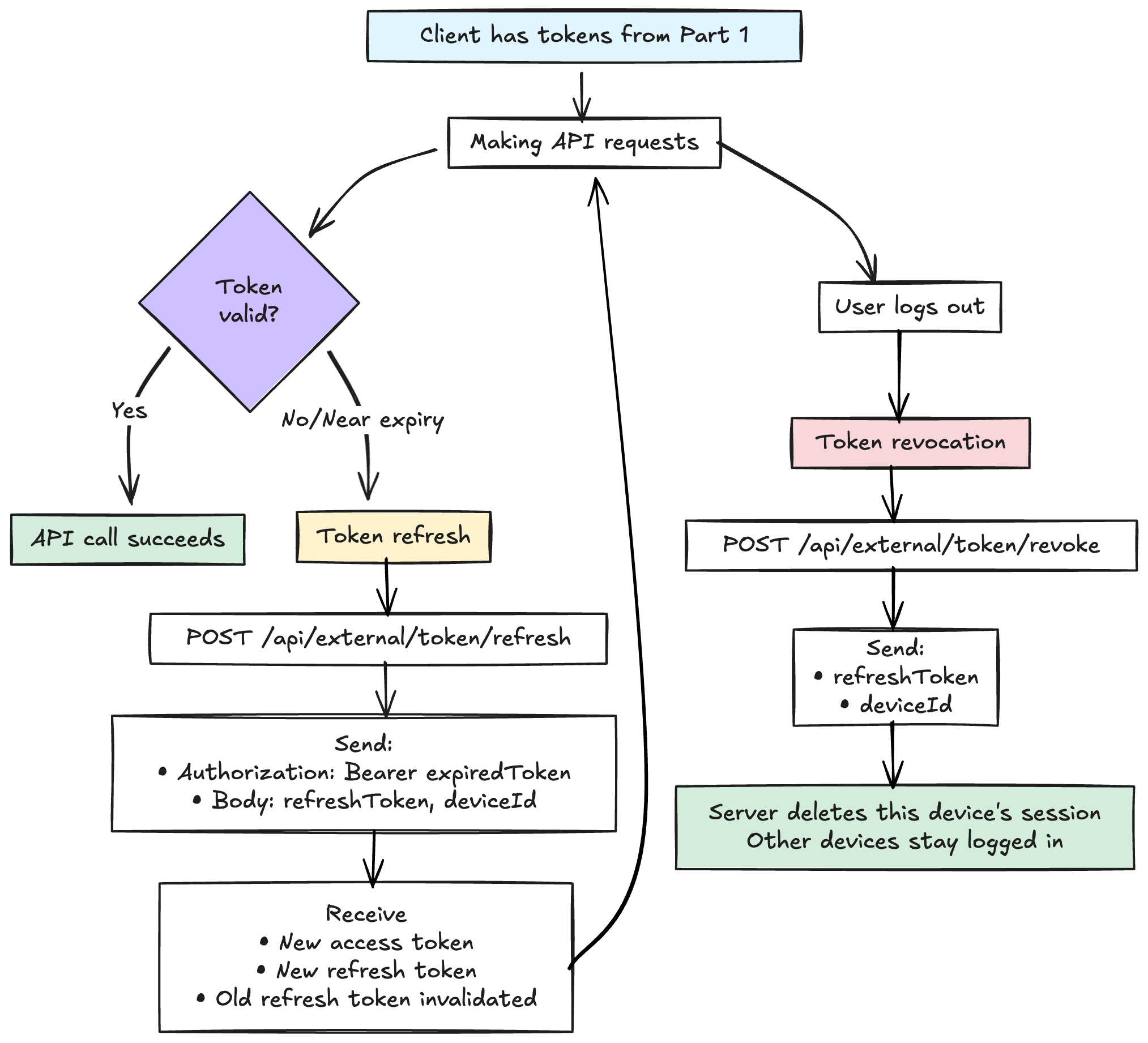
Update app/src/auth/external/api.ts:
import type {
GenerateExternalToken,
RefreshExternalToken,
RevokeExternalToken,
} from "wasp/server/api";
import { HttpError } from "wasp/server";
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import jwt from "jsonwebtoken";
import { generateTokenForUser, type JwtPayload } from "./core";
const ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS =
process.env.ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS?.split(",")
.map(id => id.trim())
.filter(Boolean) || [];
const JWT_SECRET = process.env.JWT_SECRET;
/**
* Generate tokens via API (alternative to Wasp action)
* Requires valid Wasp session cookie
* Most apps should use the Wasp action instead - this is for advanced cases
*/
export const generateExternalToken: GenerateExternalToken = async (
req,
res,
context
) => {
// Verify the user is authenticated via Wasp session
if (!context.user) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Not authenticated");
}
// Validate origin as defense-in-depth (CORS should handle this first)
const origin = req.headers.origin;
if (
origin &&
!origin.startsWith("http://localhost") &&
!origin.startsWith("chrome-extension://")
) {
throw new HttpError(403, "Invalid origin");
}
// Get parameters
const { deviceId, clientId } = req.body;
if (!deviceId || typeof deviceId !== "string") {
throw new HttpError(400, "Missing or invalid deviceId");
}
// Validate client ID against allowlist
if (clientId) {
if (!ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS.includes(clientId)) {
throw new HttpError(403, "Unauthorized client ID");
}
}
// Generate tokens using the user ID from context
const tokens = await generateTokenForUser(
context.user.id,
deviceId,
context.entities
);
return res.json(tokens);
};
/**
* Refresh access token using refresh token
* Requires Authorization header with expired access token
*/
export const refreshExternalToken: RefreshExternalToken = async (
req,
res,
context
) => {
const { refreshToken, deviceId } = req.body;
const authHeader = req.headers.authorization;
// Validate input
if (!refreshToken || !deviceId) {
throw new HttpError(400, "Missing refreshToken or deviceId");
}
if (typeof refreshToken !== "string" || typeof deviceId !== "string") {
throw new HttpError(400, "Invalid refreshToken or deviceId format");
}
if (!authHeader || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Missing or invalid Authorization header");
}
// Extract and decode the expired access token to get userId
const expiredAccessToken = authHeader.substring(7);
let userId: string;
try {
// Decode without verification since we expect it to be expired
const decoded = jwt.decode(expiredAccessToken) as { userId: string } | null;
if (!decoded || !decoded.userId) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Invalid access token format");
}
userId = decoded.userId;
} catch (err) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Invalid access token");
}
// Look up session using unique constraint on (userId, deviceId)
const session = await context.entities.UserExternalSession.findUnique({
where: {
userId_deviceId: {
userId,
deviceId,
},
},
include: { user: true },
});
if (!session) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Invalid refresh token");
}
// Verify the refresh token
const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(
refreshToken,
session.hashedRefreshToken
);
if (!isValid) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Invalid refresh token");
}
// Check expiration
if (new Date() > session.expiresAt) {
// Clean up expired session
await context.entities.UserExternalSession.delete({
where: { id: session.id },
});
throw new HttpError(401, "Refresh token expired");
}
// Generate new token pair
// This invalidates the old refresh token (via upsert in generateTokenForUser)
const tokens = await generateTokenForUser(
session.userId,
deviceId,
context.entities
);
return res.json(tokens);
};
/**
* Revoke all device sessions for the user
* Client can explicitly log out by revoking their tokens
*//**
* Revoke a specific device session
* Client can explicitly log out by revoking their tokens
*/
export const revokeExternalToken: RevokeExternalToken = async (
req,
res,
context
) => {
const { refreshToken, deviceId } = req.body;
// Validate input
if (!refreshToken || !deviceId) {
throw new HttpError(400, "Missing refreshToken or deviceId");
}
if (typeof refreshToken !== "string" || typeof deviceId !== "string") {
throw new HttpError(400, "Invalid refreshToken or deviceId format");
}
// Find all sessions for this device
const sessions = await context.entities.UserExternalSession.findMany({
where: { deviceId },
});
// Find and delete the matching session
for (const session of sessions) {
const isValid = await bcrypt.compare(
refreshToken,
session.hashedRefreshToken
);
if (isValid) {
await context.entities.UserExternalSession.delete({
where: { id: session.id },
});
return res.json({
success: true,
message: "Session revoked",
});
}
}
// Even if token not found, return success (prevents enumeration)
// Revocation is idempotent
return res.json({ success: true, message: "Session revoked" });
};
Why use findUnique with userId_deviceId?
The database enforces a unique constraint on (userId, deviceId), which means there can only be one session per user per device. Using findUnique with this composite key performs an O(1) direct lookup instead of retrieving multiple rows and looping through them. This is more efficient and leverages the database’s indexing.
Why refresh requires the Authorization header:
The expired access token contains the userId in its payload. By requiring this header, we can decode the token (without verification, since it’s expired) to extract the userId for the session lookup. This eliminates the need to iterate through sessions and makes the lookup more efficient using the unique constraint.
Token revocation scope:
This implementation revokes only the specific device session, not all of the user’s sessions. When a user signs out on one device (like their Chrome extension), they remain logged in on their other devices. This provides better UX—users can manage each device independently.
If you need to revoke all sessions for a user at once (for example, when a user changes their password or reports a compromised account), you can modify the implementation to delete all sessions by userId instead of just the matching session by id.
Automatic token rotation:
When you refresh, generateTokenForUser issues a new refresh token and replaces the old one in the database. This means each refresh token can only be used once. If someone steals a refresh token and uses it, the legitimate client’s next refresh will fail, alerting the user to potential compromise.
Idempotent revocation:
Whether the token exists or not, revocation returns success. This prevents attackers from using revocation to enumerate valid tokens. It’s also better UX—if a user clicks “log out” twice, both requests succeed.
Explicit expiration checks:
Even though expired tokens won’t verify normally, we explicitly check and clean up expired sessions. This defense-in-depth approach ensures expired sessions can’t be used even if there’s a bug elsewhere.
Step 3: Token Validation and Shared Utilities
Now that we can generate, refresh, and revoke tokens, we need two more pieces:
- Middleware to validate tokens on protected API endpoints
- Shared validation utilities for client IDs and redirect URIs
Token Validation Middleware
When your external client makes API requests with an access token, you need to verify that token and extract the user information. Create app/src/auth/external/tokenValidation.ts:
import type { Request } from "express";
import { HttpError } from "wasp/server";
import { verifyExternalJwt, type JwtPayload } from "./core";
/**
* Extract and verify Bearer token from Authorization header
* Returns the decoded token payload
*
* @throws {HttpError} If token is missing, invalid, expired, or device ID mismatch
*/
export async function verifyExternalToken(
req: Request,
context: any
): Promise<JwtPayload> {
const authHeader = req.headers.authorization;
const deviceId = req.headers["x-device-id"] as string | undefined;
if (!authHeader || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Missing or invalid Authorization header");
}
if (!deviceId) {
throw new HttpError(401, "Missing X-Device-ID header");
}
const token = authHeader.substring(7); // Remove 'Bearer ' prefix
// verifyExternalJwt handles:
// - JWT signature verification (later, we'll add per-user JWT verification)
// - Device ID validation (token deviceId must match header deviceId)
// - Session existence check (ensures session hasn't been revoked)
return await verifyExternalJwt(token, deviceId, context);
}
/**
* Middleware factory for protecting API endpoints
* Use this in your Wasp API endpoint handlers
*/
export async function requireExternalAuth(
req: Request,
context: any
): Promise<JwtPayload> {
return await verifyExternalToken(req, context);
}
Using Token Validation in Your API Endpoints
Now you can protect any API endpoint by validating the token.
Security Considerations for Token Validation
- The JWT library automatically checks expiration, but if you’re decoding without verification (like in the refresh endpoint), never use an expired token to authorize actions.
- The token includes deviceId, which you can use for:
- Logging which device made the request
- Implementing per-device rate limiting
- Displaying “last accessed from device X” to users
Client ID and Redirect URI Validation
Both your authorization page and API endpoints need to validate our specific external client, Chrome extension IDs and redirect URIs. Create app/src/utils/chromeExtensionValidation.ts:
const ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS =
process.env.ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS?.split(",")
.map(id => id.trim())
.filter(Boolean) || [];
/**
* Validate Chrome extension ID format and allowlist
*
* Note: In a Wasp app, you'd typically import from wasp/server and use
* env.ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS for typed environment variable access
* rather than process.env directly. This example uses process.env for clarity.
*/
export function validateExtensionId(extensionId: string): boolean {
if (!extensionId || typeof extensionId !== "string") {
return false;
}
// Chrome extension IDs are 32 lowercase hexadecimal characters (a-p only)
if (!/^[a-p]{32}$/.test(extensionId)) {
return false;
}
// If no allowlist configured (dev), accept any valid format
if (ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS.length === 0) {
return true;
}
// Check against allowlist
return ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS.includes(extensionId);
}
/**
* Extract extension ID from chrome-extension:// URL
*/
export function extractExtensionId(url: string): string | null {
if (!url.startsWith("chrome-extension://")) {
return null;
}
const match = url.match(/^chrome-extension:\/\/([a-p]{32})/);
return match ? match[1] : null;
}
/**
* Validate redirect URI matches the extension
* Supports both chrome-extension:// and https://<extension-id>.chromiumapp.org/ formats
*/
export function validateRedirectUriForExtension(
redirectUri: string,
extensionId: string
): {
isValid: boolean;
error?: string;
} {
try {
const url = new URL(redirectUri);
// Support chrome-extension:// protocol
if (url.protocol === "chrome-extension:") {
// Extract extension ID from redirect URI
const uriExtensionId = extractExtensionId(redirectUri);
if (!uriExtensionId) {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "Invalid extension ID in redirect URI",
};
}
// Must match the client's extension ID exactly
if (uriExtensionId !== extensionId) {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "Redirect URI extension ID must match client_id",
};
}
return { isValid: true };
}
// Support https://<extension-id>.chromiumapp.org/ format
if (
url.protocol === "https:" &&
url.hostname.endsWith(".chromiumapp.org")
) {
const hostnameExtensionId = url.hostname.split(".")[0];
if (!/^[a-p]{32}$/.test(hostnameExtensionId)) {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "Invalid extension ID format in chromiumapp.org URL",
};
}
if (hostnameExtensionId !== extensionId) {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "chromiumapp.org extension ID must match client_id",
};
}
return { isValid: true };
}
// Block javascript: and data: URIs
if (url.protocol === "javascript:" || url.protocol === "data:") {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "Invalid protocol in redirect URI",
};
}
return {
isValid: false,
error:
"Redirect URI must use chrome-extension:// or https://<extension-id>.chromiumapp.org/ format",
};
} catch (err) {
return {
isValid: false,
error: "Invalid URL format",
};
}
}
Create app/src/utils/redirectValidation.ts:
/**
* Verify redirect URI doesn't point to the authorization page
*
* Note: This is a simplified version for the blog. Production implementations
* should handle additional edge cases like protocol-relative URLs (//example.com),
* absolute URLs with different origins, and other URL parsing edge cases.
*/
export function verifyNoRedirectLoop(redirectUri: string): boolean {
try {
const url = new URL(redirectUri);
return !url.pathname.includes("/auth/external/authorize");
} catch {
return false;
}
}
Having validation in one place ensures that client and server use identical rules, prevents logic divergence, and allows for independent testing.
Step 4: Complete Environment Configuration
Update your .env.server with all required variables:
# JWT Secret (required)
# Must be the same as your main Wasp auth JWT secret
JWT_SECRET=your-super-secret-jwt-key-min-32-chars-long-and-random
# Allowed Chrome Extension IDs (required in all environments)
# Comma-separated list of extension IDs that can authorize
# Get these from chrome://extensions
# Format: 32 lowercase letters, no spaces in the IDs themselves
ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS=abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz123456,zyxwvutsrqponmlkjihgfedcba654321
# Node environment (auto-set by Wasp in production)
NODE_ENV=development
External Client Configuration
In your extension (or mobile app, etc), create a config file:
// config.js
export const config = {
// Your Wasp app URL (no trailing slash)
apiUrl:
process.env.NODE_ENV === "production"
? "https://yourapp.com"
: "http://localhost:3000",
// Authorization endpoint
authUrl:
process.env.NODE_ENV === "production"
? "https://yourapp.com/auth/external/authorize"
: "http://localhost:3000/auth/external/authorize",
};
Step 5: Chrome Extension Integration
Now let’s see how your Chrome extension uses these tokens. Here’s a complete implementation.
Extension Background Script
// background.js or background/auth.js
import { config } from "./config";
/**
* Authenticate user via OAuth flow
*/
export async function authenticateUser() {
const extensionId = chrome.runtime.id;
// Construct redirect URI
const redirectUri = `chrome-extension://${extensionId}/auth/callback.html`;
// Generate CSRF token
const state = generateRandomString(32);
await chrome.storage.local.set({ auth_state: state });
// Build authorization URL
const authUrl = new URL(config.authUrl);
authUrl.searchParams.set("client_id", extensionId);
authUrl.searchParams.set("redirect_uri", redirectUri);
authUrl.searchParams.set("state", state);
try {
// Launch web auth flow
const redirectUrl = await chrome.identity.launchWebAuthFlow({
url: authUrl.toString(),
interactive: true,
});
// Parse tokens from URL fragment
const fragment = redirectUrl.split("#")[1];
if (!fragment) {
throw new Error("No tokens received");
}
const params = new URLSearchParams(fragment);
const accessToken = params.get("access_token");
const refreshToken = params.get("refresh_token");
const expiresIn = params.get("expires_in");
const returnedState = params.get("state");
// Verify state (CSRF protection)
const { auth_state } = await chrome.storage.local.get("auth_state");
if (returnedState !== auth_state) {
throw new Error("State mismatch - possible CSRF attack");
}
// Store tokens securely
await chrome.storage.local.set({
accessToken,
refreshToken,
tokenExpiry: Date.now() + parseInt(expiresIn) * 1000,
});
// Clean up state
await chrome.storage.local.remove("auth_state");
console.log("Authentication successful!");
return { success: true };
} catch (error) {
console.error("Authentication failed:", error);
throw error;
}
}
/**
* Make authenticated API request with automatic token refresh
*/
export async function makeAuthenticatedRequest(endpoint, options = {}) {
const { accessToken, refreshToken, tokenExpiry } =
await chrome.storage.local.get([
"accessToken",
"refreshToken",
"tokenExpiry",
]);
if (!accessToken || !refreshToken) {
throw new Error("Not authenticated. Please sign in.");
}
// Check if token needs refresh (5 minutes before expiry)
const needsRefresh = Date.now() >= tokenExpiry - 5 * 60 * 1000;
if (needsRefresh) {
await refreshAccessToken();
return makeAuthenticatedRequest(endpoint, options);
}
// Make request with access token
const response = await fetch(`${config.apiUrl}${endpoint}`, {
...options,
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
"Content-Type": "application/json",
...options.headers,
},
});
// If 401, try refresh once
if (response.status === 401) {
await refreshAccessToken();
return makeAuthenticatedRequest(endpoint, options);
}
return response;
}
/**
* Refresh access token
*/
async function refreshAccessToken() {
const { refreshToken, accessToken } = await chrome.storage.local.get([
"refreshToken",
"accessToken",
]);
const deviceId = await getDeviceId();
if (!refreshToken || !accessToken) {
throw new Error("No refresh token available");
}
try {
const response = await fetch(
`${config.apiUrl}/api/external/token/refresh`,
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
body: JSON.stringify({ refreshToken, deviceId }),
}
);
if (!response.ok) {
await chrome.storage.local.remove([
"accessToken",
"refreshToken",
"tokenExpiry",
]);
throw new Error("Session expired. Please sign in again.");
}
const tokens = await response.json();
await chrome.storage.local.set({
accessToken: tokens.accessToken,
refreshToken: tokens.refreshToken,
tokenExpiry: Date.now() + tokens.expiresIn * 1000,
});
console.log("Token refreshed successfully");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Token refresh failed:", error);
throw error;
}
}
/**
* Sign out
*/
export async function signOut() {
const { refreshToken } = await chrome.storage.local.get("refreshToken");
const deviceId = await getDeviceId();
if (refreshToken) {
try {
await fetch(`${config.apiUrl}/api/external/token/revoke`, {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ refreshToken, deviceId }),
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("Revocation failed:", error);
}
}
await chrome.storage.local.remove([
"accessToken",
"refreshToken",
"tokenExpiry",
]);
console.log("Signed out successfully");
}
/**
* Get or generate device ID
*/
async function getDeviceId() {
const { deviceId } = await chrome.storage.local.get("deviceId");
if (deviceId) return deviceId;
const newDeviceId = crypto.randomUUID();
await chrome.storage.local.set({ deviceId: newDeviceId });
return newDeviceId;
}
/**
* Generate random string for CSRF
*/
function generateRandomString(length) {
const array = new Uint8Array(length);
crypto.getRandomValues(array);
return Array.from(array, byte => byte.toString(16).padStart(2, "0")).join("");
}
Extension Callback Page
Create auth/callback.html:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Authentication Callback</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Authentication successful! You can close this window.</p>
<script>
// This page exists only as a redirect target
// Chrome will close it automatically
</script>
</body>
</html>
Extension Manifest
{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "Your Extension",
"version": "1.0.0",
"permissions": ["storage", "identity"],
"host_permissions": ["http://localhost:3000/*", "https://yourapp.com/*"],
"background": {
"service_worker": "background.js",
"type": "module"
},
"web_accessible_resources": [
{
"resources": ["auth/callback.html"],
"matches": ["<all_urls>"]
}
]
}
Testing the Complete Flow
1. Set Your Extension ID
Get your extension ID from chrome://extensions and add to .env.server:
ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS=your-extension-id-here
Restart Wasp to pick up the change.
2. Test Authentication
In your extension:
await authenticateUser();
You should see:
- Browser window opens to your Wasp app
- Sign in if needed
- “Authorizing application…” message
- Window closes automatically
- Tokens stored in chrome.storage
3. Test API Calls
const response = await makeAuthenticatedRequest("/api/some-endpoint");
console.log(await response.json());
Check server logs for:
[CORS] Allowed extension: chrome-extension://your-extension-id
4. Test Token Refresh
Wait for expiry (or set sooner expiry for testing), then make another request, the token should automatically refresh.
5. Test Revocation
await signOut();
Check the database—the UserExternalSession row for this specific device should be deleted, but other sessions remain.
Troubleshooting
CORS Errors
Check:
- Extension ID in
ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS? - Restarted Wasp after env change?
- Environment variable actually set?
Add logging to middleware:
console.log("Allowed IDs:", ALLOWED_CHROME_EXTENSION_IDS);
console.log("Received origin:", origin);
401 on Token Refresh
Check:
- Authorization header included with expired access token?
- Device ID consistent?
- Refresh token expired (7 days)?
- Session deleted from database?
SELECT * FROM "UserExternalSession" WHERE "deviceId" = 'your-device-id';
Tokens Not Persisting
Check:
storagepermission in manifest?- Awaiting
chrome.storageoperations? - Using
chrome.storage.local(notlocalStorage)?
Debug:
chrome.storage.local.get(null, items => {
console.log("All storage:", items);
});
What’s Next
In Part 3, we’ll add per-user JWT secrets for enterprise-grade security:
- Granular revocation (invalidate all tokens for one user)
- Reduced blast radius if secrets leak
- User-specific signing keys
About the Author
I’m Rachel Cantor, a fullstack engineer with over 13 years of experience building production systems that scale.
I am beginning to take on new consulting clients for any number of projects—authentication systems, component libraries, internal tooling, or technical architecture that requires someone with a knack for detail, who can both design a system, ship production code, and make it all look great.
If you’re dealing with:
- Design systems or component libraries that need to scale
- Chrome extensions or cross-platform integrations
- Internal tools your team hasn’t had bandwidth to build properly
Feel free to reach out to me on LinkedIn while I work on making a proper intake form.